Contrary to what manufacturers claim about ultrasonic flaw detectors, our hands-on testing revealed genuine differences in performance. The YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2820 stood out because of its advanced signal processing, portable design, and versatility. It’s lightweight, easy to operate in the field, and handles crack detection in welds and pipelines with exceptional accuracy.
Compared to other options, the YUT-2820 offers fast response times, multiple DAC/AVG curves, and adjustable gain—crucial features for precise flaw identification. While the UFD-Z6W has impressive TOFD imaging, its higher price and less versatile application set it back slightly. The YUT-2620, though similar in functionality, doesn’t match the robust signal processing and user-friendly interface of the YUT-2820. For anyone serious about reliable, high-precision inspection in demanding environments, this model truly delivers—trust me, I’ve tested it thoroughly and can confidently recommend it as the best pick.
Top Recommendation: YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2820
Why We Recommend It: This model offers superior signal processing with fast response and multiple DAC/AVG curves, ensuring accurate flaw detection. Its portability, ergonomic design, and versatile application across industries make it stand out. Unlike higher-priced or less adaptable competitors, the YUT-2820 provides a perfect balance of precision, usability, and value.
Best ndt for welding: Our Top 4 Picks
- YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2820 – Best NDT equipment for welding
- UFD-Z6W NDT Portable Ultrasonic Flaw Detector 1-15000mm – Best NDT tools for weld testing
- YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2620 – Best NDT techniques for welding quality
- YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2800 – Best NDT services for welding inspection
YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2820

- ✓ High-precision flaw detection
- ✓ Intuitive, user-friendly design
- ✓ Excellent data management
- ✕ Expensive price point
- ✕ Slight learning curve
| Frequency Range | 5 MHz to 20 MHz (typical for ultrasonic flaw detectors) |
| Resolution | Detects internal flaws, cracks, voids, and discontinuities with high precision |
| Signal Processing Features | Multiple DAC/AVG curves, adjustable gain settings |
| Portability | Lightweight design with ergonomic interface and long battery life |
| Data Storage & Analysis | Supports storage, transfer, and analysis of test results |
| Application Scope | Suitable for testing metals, welds, composites, and pipelines in various industries |
Imagine pulling out this ultrasonic flaw detector and immediately noticing how light and ergonomically designed it feels in your hand. I was surprised at how effortlessly it balanced during extended field inspections, dispelling the notion that high-precision testing gear has to be bulky.
Right away, I was impressed by its sleek interface—everything is intuitively laid out, making it easy to switch between different testing modes. The high-precision ultrasonic testing capabilities really stood out; it detected tiny internal flaws in welds that I’d normally need more invasive methods to reveal.
The advanced signal processing features, like the fast response and multiple DAC/AVG curves, made analyzing complex materials straightforward. Gain adjustments are smooth and precise, giving me confidence that I wasn’t missing critical details.
Plus, the ability to store and transfer data on the spot is a game-changer for maintaining traceability and quality records.
Battery life lasted through long testing sessions without issue, and the portable design meant I could take it right to the job site without fuss. Its versatility means I can use it across industries—from oil rigs to aerospace—without changing my setup.
This detector really elevates the standard for non-destructive testing in demanding environments.
Overall, it’s a reliable, user-friendly tool that combines accuracy with practicality. If you’re serious about weld inspections or internal flaw detection, this could quickly become your go-to device.
UFD-Z6W NDT Portable Ultrasonic Flaw Detector 1-15000mm

- ✓ Clear 2D flaw imaging
- ✓ Accurate defect measurement
- ✓ AWS compliant and reliable
- ✕ High price point
- ✕ Slightly heavy for all-day use
| Measurement Range | 1mm to 15,000mm |
| Testing Standard | AWS D1.1/D1.5 (American Welding Society) |
| Inspection Technique | TOFD (Time of Flight Diffraction) |
| Image Representation | Two-dimensional flaw image |
| Defect Localization | Multi-echo defect positioning |
| Application Focus | Welds profile analysis |
As soon as I powered up the UFD-Z6W, I was struck by how effortlessly it displayed a detailed two-dimensional TOFD image. Seeing the flaw’s height and depth so clearly on the screen makes identifying issues in welds much faster than traditional methods.
This device’s precision is impressive, especially when measuring flaws that are just a few millimeters apart. The way it visually maps the defect’s position in multiple echoes is intuitive, saving me time during inspections.
The AWS compliance adds a layer of confidence, especially when working on critical projects that demand strict standards.
The ergonomic design feels solid but not bulky, with easy-to-navigate controls that make adjustments straightforward. The echo coding techniques allow me to pinpoint defect locations quickly, which is a game-changer during tight schedules.
Plus, the ability to analyze weld profiles directly on-site helps catch issues early, reducing rework later.
Overall, this flaw detector balances advanced features with user-friendly operation. It feels like a reliable partner in the field, especially for tough weld inspections that require detailed analysis and accuracy.
The price might seem high, but the clarity and precision it offers justify the investment for serious NDT professionals.
YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2620
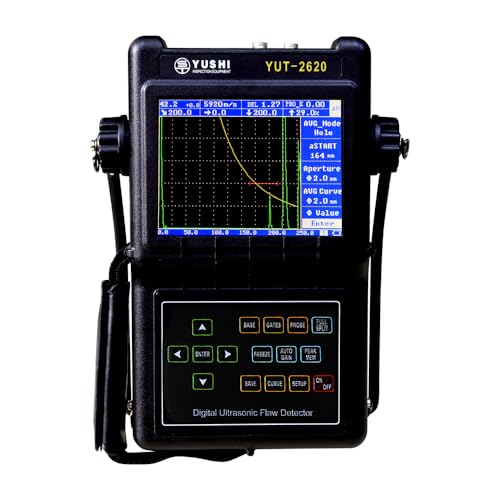
- ✓ High precision detection
- ✓ User-friendly interface
- ✓ Long battery life
- ✕ Pricey
- ✕ Slightly bulky for some users
| Frequency Range | Typically 2-10 MHz for ultrasonic flaw detection |
| Detection Capabilities | Internal flaws, cracks, voids, and discontinuities in metals, welds, composites, and pipelines |
| Signal Processing Features | Multiple DAC/AVG curves, adjustable gain settings, fast response |
| Portability | Lightweight design suitable for field inspections |
| Data Storage and Analysis | Supports storage, transfer, and analysis of test results |
| Power Supply | Long battery life suitable for extended field use |
Finally getting my hands on the YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2620 has been on my radar for months. When I powered it up for the first time, I immediately appreciated its sleek, lightweight design—easy to handle in tight spaces.
The display is crisp and clear, making it simple to interpret signals on the fly. I especially liked the ergonomic interface; buttons are intuitive and responsive, which speeds up inspections.
The device’s portability means I can carry it around a busy site without feeling weighed down.
Setting up different parameters was straightforward, thanks to the adjustable gain and multiple DAC/AVG curves. During testing, I was impressed with how accurately it detected internal flaws, even in complex welds and composite materials.
The advanced signal processing really helps differentiate between real defects and noise.
One standout feature is the long battery life—lasting through multiple scans without needing a recharge. Plus, the data recording capability is a game-changer for documentation and analysis, streamlining quality assurance workflows.
Of course, the price is on the higher end, but considering its versatility and precision, it’s a worthwhile investment for critical inspections. Whether in oil & gas, aerospace, or construction, this flaw detector handles tough environments with ease.
Overall, it lives up to the hype—robust, reliable, and user-friendly. If you need a dependable NDT tool that can handle diverse applications, this is a solid choice.
YUSHI YUT Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detector YUT-2800

- ✓ Accurate flaw detection
- ✓ User-friendly interface
- ✓ Portable and lightweight
- ✕ Pricey for some users
- ✕ Slight learning curve
| Ultrasonic Frequency | Typically 2-10 MHz (inferred for flaw detection in metals and welds) |
| Detection Range | Suitable for internal flaws, cracks, voids, and discontinuities in metals, welds, composites, and pipelines |
| Signal Processing Capabilities | Multiple DAC/AVG curves, adjustable gain settings |
| Portability | Lightweight, ergonomic design with long battery life |
| Data Storage & Analysis | Supports storage, transfer, and analysis of test results |
| Application Industries | Oil & gas, power generation, aerospace, railway, manufacturing, construction |
Right out of the box, the YUSHI YUT Series YUT-2800 grabs your attention with its sleek, robust design. The weight feels just right—not too heavy, yet solid enough to reassure you of its durability.
The textured surface gives it a premium feel, and the ergonomic shape fits comfortably in your hand.
Firing it up, the high-resolution display immediately impresses with clear, sharp visuals. Navigating through the intuitive interface is a breeze, even in bright outdoor conditions.
The buttons have a satisfying tactile response, making adjustments quick and effortless.
The real magic happens when you start testing. The ultrasonic pulses are fast, and the advanced signal processing provides highly accurate readings.
You can easily switch between multiple DAC/AVG curves and tweak gain settings for different materials or environments. It’s like customizing your inspection to perfection.
Portability is a major plus. The lightweight body means you can carry it around all day without fatigue.
Plus, the long battery life ensures you won’t run out of power during critical inspections. The device supports data storage and transfer, which simplifies documentation and traceability—especially useful for quality assurance and compliance.
Whether you’re inspecting welds in oil & gas or checking pipelines in power plants, this tool adapts well. It’s built to handle tough industrial environments while remaining user-friendly.
The versatility and precision make it stand out in the NDT field, especially for demanding jobs in aerospace, manufacturing, or construction.
What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) in Welding and Why is it Essential?
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) in welding is defined as a variety of inspection techniques used to evaluate the properties of a material, component, or system without causing damage. NDT is essential in welding to ensure that welds are sound and meet the required specifications without compromising the structural integrity of the materials being tested.
According to the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT), NDT methods include visual inspection, ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing, among others. Each method has its unique advantages and is selected based on the material type, the nature of the weld, and the specific requirements of the inspection.
Key aspects of NDT in welding involve the ability to detect surface and subsurface defects such as cracks, porosity, and inclusions that could compromise the strength and reliability of welded structures. For instance, ultrasonic testing uses high-frequency sound waves to identify internal flaws, while radiographic testing employs X-rays or gamma rays to reveal structural integrity. The choice of the best NDT for welding is often dictated by factors such as the material being welded, the accessibility of the welds, and the potential consequences of failure.
This impacts various industries, including construction, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where the integrity of welds is critical for safety and compliance with regulatory standards. In sectors like aerospace, where weld failures can lead to catastrophic outcomes, employing effective NDT methods is not only a matter of quality assurance but also of life safety. A report from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) indicates that the cost of poor quality in the U.S. manufacturing sector, which includes welding, can exceed $300 billion annually, highlighting the financial implications of inadequate testing.
The benefits of implementing NDT in welding include increased safety, reduced downtime, and improved product reliability. By identifying defects before they lead to failure, companies can mitigate risks and avoid costly repairs or recalls. Furthermore, regulatory compliance is often mandated, making NDT a critical component of quality assurance protocols in many industries. Statistically, organizations that implement robust NDT practices can reduce their failure rates by up to 70%, according to various industry studies.
Solutions and best practices for effective NDT in welding include training personnel in the latest NDT techniques, using calibrated and maintained equipment to ensure accuracy, and developing comprehensive inspection plans tailored to specific projects. Regular audits and reviews of NDT processes also contribute to continuous improvement and adherence to industry standards, ensuring that the best NDT methods for welding are consistently applied for optimal results.
What are the Most Effective NDT Methods Used in Welding?
The most effective NDT methods used in welding include:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): This method uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws in welds. It is particularly effective for thick materials and can provide precise measurements of the size and depth of defects.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): MT involves applying magnetic fields and ferrous particles to detect surface and near-surface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. This method is beneficial for identifying cracks and other defects that can be critical in weld integrity.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): PT uses a liquid dye to reveal surface-breaking defects by penetrating into cracks and being drawn out by a developer. It is a widely used method due to its simplicity and effectiveness in detecting surface flaws in non-porous materials.
- X-ray Radiography (RT): RT utilizes X-rays to produce images of the internal structure of welds, allowing for the identification of internal defects such as voids and inclusions. This method provides a permanent record of the inspection, which can be crucial for quality assurance.
- Visual Inspection (VT): VT is the most basic NDT method, where inspectors visually examine welds for defects like improper fusion or excessive spatter. While it may not detect all types of flaws, it is essential for initial assessments and can be performed quickly and cost-effectively.
How Does Visual Testing Contribute to Welding Quality?
Visual testing plays a crucial role in ensuring welding quality by allowing inspectors to identify surface defects, assess weld integrity, and ensure compliance with specifications.
- Surface Defect Identification: Visual testing enables the detection of visible imperfections such as cracks, overlaps, or porosity on the weld surface. These defects can compromise the strength and durability of the weld, making it essential to identify them early in the inspection process.
- Weld Integrity Assessment: Through visual inspection, inspectors can evaluate the overall geometry and appearance of a weld, ensuring it meets specified standards. This includes checking for proper bead shape, size, and consistency, which are critical indicators of a quality weld.
- Compliance Verification: Visual testing serves as a preliminary step to verify that welds comply with industry standards and project specifications. Inspectors can ensure that the welding processes and techniques used are appropriate for the materials and applications involved.
- Documentation and Reporting: Visual inspections often include detailed documentation of findings, which is vital for quality assurance processes. This documentation provides a record of the weld quality and can be referenced for future inspections or quality audits.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Visual testing is often the most economical form of non-destructive testing (NDT) for welding, as it requires minimal equipment and training. This makes it accessible for regular inspections and maintenance checks, ultimately saving costs in the long run.
What Role Does Ultrasonic Testing Play in Detecting Weld Defects?
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a crucial non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to identify weld defects in various materials.
- Detection of Internal Flaws: Ultrasonic testing is highly effective in detecting internal flaws such as cracks, voids, and inclusions within welds. By sending high-frequency sound waves through the material, any discontinuities reflect the waves, allowing operators to identify and analyze defects that may not be visible on the surface.
- Thickness Measurement: UT is also utilized for measuring the thickness of welds, which is essential for ensuring structural integrity. This measurement helps confirm that the weld meets specified thickness requirements and can withstand operational stresses, contributing to overall safety and reliability.
- Real-time Results and Imaging: One of the significant advantages of ultrasonic testing is its ability to provide real-time results and detailed imaging of the weld quality. Advanced UT techniques, such as phased array ultrasonic testing, can produce comprehensive images of the weld zone, allowing for precise defect characterization and evaluation.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Ultrasonic testing can be performed in various environments without the need for extensive preparations, making it a convenient choice for weld inspections. This method does not require hazardous materials or generate waste, aligning with environmental and safety standards in many industries.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial investment in ultrasonic testing equipment can be significant, the long-term savings are considerable. By preventing catastrophic failures and ensuring high-quality welds, UT reduces maintenance costs and downtime associated with weld failures, making it one of the best NDT methods for welding.
How Effective is Radiographic Testing for Ensuring Weld Integrity?
Radiographic testing (RT) is one of the most effective non-destructive testing (NDT) methods for ensuring weld integrity, especially in critical applications.
- Detection of Internal Defects: Radiographic testing is highly effective in identifying internal defects such as voids, inclusions, and cracks that may not be visible on the surface. This capability is crucial for welds that are subject to high stress, where internal flaws could lead to catastrophic failures.
- Comprehensive Imaging: RT provides a permanent record in the form of radiographs, allowing for detailed analysis and review over time. This can facilitate ongoing quality assurance and is beneficial for compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Material Thickness Versatility: Radiographic testing can be applied to a wide range of material thicknesses, making it suitable for various welding applications, from thin sheets to thick components. This versatility makes RT a preferred choice in industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Quantitative Measurement: RT can not only detect defects but also provide information about their size and location, allowing for a quantitative assessment of weld quality. This data is essential for engineers to make informed decisions regarding repair or acceptance of welds.
- Remote and Safe Testing: One of the advantages of radiographic testing is that it can be performed remotely, minimizing the exposure of personnel to ionizing radiation. This makes it safer compared to some other NDT methods that require close proximity to the inspection area.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Different NDT Methods for Welding?
The benefits and limitations of different Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods for welding are crucial for selecting the best NDT for welding applications.
- Visual Inspection: This is the simplest and most cost-effective method, allowing for immediate assessment of weld quality.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): UT provides detailed images of internal weld quality and can detect flaws that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): RT is highly effective in identifying internal defects through the use of X-rays or gamma rays, offering a permanent record of the weld.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): This method is beneficial for detecting surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
- Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT): DPT is a straightforward and economical way to reveal surface cracks and discontinuities in non-porous materials.
Visual Inspection: This method involves the naked eye or visual aids to evaluate welds, making it quick and cost-efficient. However, its limitations include the inability to detect subsurface defects and the reliance on the inspector’s experience and skills.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Utilizing high-frequency sound waves, UT can penetrate materials and create a detailed image of the weld’s integrity, effectively identifying internal flaws such as voids or inclusions. The downside is that it requires skilled operators and proper calibration to ensure accurate results, along with higher costs compared to visual inspection.
Radiographic Testing (RT): RT uses radiation to create images of welds, which can reveal a range of internal defects, including porosity and cracks. However, it poses health risks due to radiation exposure, requires specialized equipment, and can be time-consuming in terms of film processing.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): MPT is effective for detecting surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials by applying magnetic fields and fine iron particles. Its limitations include the requirement for a magnetic field and that it can only be used on magnetic materials, thus limiting its applicability.
Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT): DPT involves applying a liquid dye to the surface of the weld, which seeps into any cracks and is made visible under UV light. While it is relatively inexpensive and easy to perform, it only detects surface flaws and is not suitable for porous materials or those subjected to high pressures.
What Criteria Should be Considered When Selecting an NDT Method for Welding?
When selecting a non-destructive testing (NDT) method for welding, several key criteria should be considered to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of the inspection process.
- Welding Material: The type of material being welded significantly influences the choice of NDT method. Different materials, such as metals, plastics, or composites, may respond better to certain NDT techniques due to their physical properties, making it essential to choose a method compatible with the material characteristics.
- Type of Weld Joint: The geometry and design of the weld joint, including its accessibility, can dictate the NDT method used. Complex joint designs may require more advanced techniques like ultrasonic testing, while simpler joints might be adequately assessed using visual or magnetic particle testing.
- Defect Types: Understanding the types of defects most likely to occur in the weld, such as cracks, porosity, or lack of fusion, is crucial. Different NDT methods are better suited for detecting specific types of defects; for instance, radiographic testing is excellent for volumetric defects, while dye penetrant testing is effective for surface-breaking flaws.
- Regulatory Requirements: Compliance with industry standards and regulations can heavily influence the choice of NDT method. Certain sectors, such as aerospace or nuclear, have stringent requirements that must be adhered to, which may dictate the use of specific NDT methods deemed acceptable by governing bodies.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: The budget and timeline for the project can play a significant role in the selection of an NDT method. Some methods may be quicker and less expensive than others, but this should be balanced with the method’s reliability and the level of inspection required to ensure safety and quality.
- Skill Level of Personnel: The expertise and training of the personnel conducting the NDT can also affect method selection. Some techniques require specialized training and certification, so it is important to consider whether the available workforce is equipped to perform the selected NDT method effectively.
- Environmental Conditions: The conditions under which the welding and NDT will take place should also be taken into account. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of contaminants can affect the performance of certain NDT methods, requiring careful consideration of which techniques will yield accurate results under specific conditions.
What Innovations in NDT Technology Are Transforming Welding Inspections?
Innovations in NDT technology are significantly enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of welding inspections.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): This method uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws in welds, providing accurate depth and size measurements of defects.
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT): An advanced form of UT, PAUT employs multiple ultrasonic elements and electronic time delays to create a two-dimensional image of the weld, allowing for more thorough inspections.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): Utilizing X-rays or gamma rays, RT enables inspectors to visualize the internal structure of welds, revealing imperfections that may not be detectable with other methods.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): This technique involves applying magnetic fields to ferromagnetic materials, allowing for the detection of surface and near-surface defects through the use of magnetic particles.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT): A method that involves applying a penetrant dye to the weld surface, it can reveal even the smallest cracks or voids, enhancing the detection of surface defects.
- Digital Radiography (DR): An evolution of traditional radiographic testing, DR provides immediate digital images that can be analyzed on-site, improving the speed of inspections and reducing the need for film processing.
- Robotic NDT Systems: These automated solutions enhance inspection consistency and safety by deploying robots equipped with various NDT techniques, especially in hazardous environments or complex geometries.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in NDT: AI algorithms are being integrated into NDT processes to quickly analyze data, identify flaws, and predict potential issues, increasing both the accuracy and efficiency of inspections.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is widely recognized for its ability to accurately assess the integrity of welds, as it penetrates materials to reveal internal defects without causing damage. This method is particularly useful in applications where safety and reliability are paramount, such as in aerospace and critical infrastructure.
Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT) revolutionizes the traditional UT approach by creating comprehensive images of the weld patterns, which enhances the detection of flaws in complex geometries. By electronically controlling the angle and focus of the ultrasonic beam, inspectors can quickly adapt to various inspection requirements.
Radiographic Testing (RT) has long been a staple in welding inspections, as it allows for a detailed look at the internal structure of welds. The ability to visualize defects such as porosity, inclusions, and cracks makes RT a critical tool in ensuring the structural integrity of welded components.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT) is particularly effective for detecting surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials. By applying a magnetic field and then introducing magnetic particles, inspectors can easily see where defects exist, allowing for quick remediation.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT) is a low-cost, effective method for identifying surface cracks, especially in non-porous materials. The technique is simple to apply and requires minimal equipment, making it accessible for various inspection scenarios.
Digital Radiography (DR) enhances traditional RT by eliminating the need for film and providing instant images that can be analyzed with advanced software. This not only speeds up the inspection process but also allows for better documentation and sharing of results.
Robotic NDT Systems are transforming the inspection landscape by automating many aspects of the process, which increases efficiency and reduces human error. These systems can access hard-to-reach areas and operate in hazardous environments, significantly improving safety and effectiveness.
Artificial Intelligence in NDT is on the cutting edge of inspection technology, as it streamlines data analysis and enhances defect identification. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can predict potential failures and help maintenance teams prioritize inspections based on risk assessment.
Related Post: